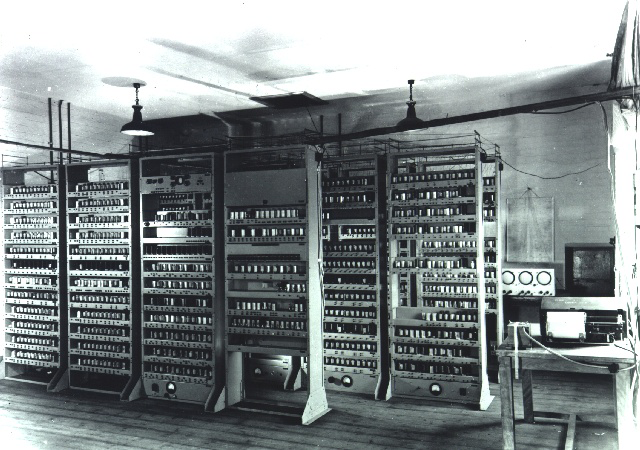
University of Cambridge EDSAC
Generation
1st
Developer
?
Launched In
1949
Decomissioned In
1958
Launch Price
$0
Games
1
The Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator (EDSAC) holds a significant place in the history of computing as one of the earliest and most influential computers.
-
Development and Introduction: EDSAC was developed at the University of Cambridge in the United Kingdom. Construction began in 1947, and it became operational in May 1949. It was designed primarily by Sir Maurice Wilkes, a British computer scientist.
-
Design and Architecture: EDSAC was a groundbreaking computer for its time, featuring a stored-program architecture. It used vacuum tubes for logic and a mercury delay line for memory storage. The computer was capable of performing a wide range of calculations and running stored programs.
-
Applications and Use: EDSAC was primarily used for scientific and mathematical computations, including calculations related to atomic energy, weather forecasting, and mathematical research. It played a significant role in advancing various fields of science and engineering.
-
Legacy and Impact: EDSAC's development marked a crucial milestone in the history of computing. It was one of the first computers to use a stored-program architecture, which became the standard for all subsequent computers. EDSAC inspired further research and development in the field of computing and laid the groundwork for subsequent generations of computers.
-
Discontinuation: EDSAC remained in operation at the University of Cambridge until 1958, after which it was decommissioned and dismantled. Despite its relatively short operational lifespan, its impact on the field of computing was profound and long-lasting.
-
Replica and Preservation: In recent years, efforts have been made to recreate and preserve EDSAC's legacy. A replica of the original EDSAC was completed in 2015 as part of the EDSAC Project, allowing researchers and enthusiasts to experience and study the historic computer firsthand.
In summary, EDSAC was a pioneering computer that played a crucial role in the early history of computing. Its innovative design and architecture laid the foundation for modern computers, and its legacy continues to be felt in the field of computing today.